The OLSAT Test in 2025
All products and services featured are independently selected by WikiJob. When you register or purchase through links on this page, we may earn a commission.
- A List of OLSAT Tests Available for Practicing in 2025
- What Is the OLSAT Test?
- Who Takes the OLSAT Test?
- What Does the OLSAT Test Measure?
- Why the OLSAT?
- OlSAT Test Format
- OLSAT Test Examples
empty
empty
empty
empty
- OLSAT Scoring
- OLSAT Test Preparation (2025)
empty
empty
- Tips for Solving OLSAT Classification Questions
empty
empty
empty
empty
empty
empty
empty
empty
- General Tips for OLSAT Test
- Should My Child Take the OLSAT Test?
- Final Thoughts
A List of OLSAT Tests Available for Practicing in 2025
- OLSAT Level A - Pre-kindergarten and Kindergarten
- OLSAT Level B - 1st Grades
- OLSAT Level C - 2nd Grades
- OLSAT Level D - 3rd Grades
- OLSAT Level E - 4th and 5th Grades
- OLSAT Level F - 6th, 7th and 8th Grades
- OLSAT Level G - 9th, 10th, 11th and 12th Grades
What Is the OLSAT Test?
The Otis-Lennon School Ability Test (OLSAT) is a multiple-choice test issued by Pearson NNC to identify highly gifted children.
The test is infamously difficult, with many adults finding it a challenge too. However, a pass in this test could grant your child admission to the most advanced learning programs in the country.
Schools have also used the OLSAT test to measure their students' academic ability across all the ages to determine how well they are performing as an institute.
The OLSAT was created to measure intelligence and focuses on speed of thought and reasoning skills. It is considered to be a very reliable measure of intelligence, as scores rarely change over time.
It is important to point out that the OLSAT is regularly peer-reviewed to reduce gender, ethnic, regional and cultural biases.
Who Takes the OLSAT Test?
The OLSAT (Otis-Lennon School Ability Test) is typically taken by students in grades pre-K through 12.
It is commonly used as a screening tool to assess students' cognitive abilities and their potential for academic success.
The test is administered by many schools and educational institutions, including both public and private schools, as well as gifted and talented programs.
What Does the OLSAT Test Measure?
The OLSAT (Otis-Lennon School Ability Test) measures several areas of cognitive ability. These areas assess a student's aptitude for learning and academic success. Here are the main areas typically measured by the OLSAT:
- Verbal Comprehension: This area measures a student's ability to understand and work with verbal information. It includes tasks such as identifying similarities and differences between words, understanding word meanings and reasoning with verbal concepts.
- Verbal Reasoning: Verbal reasoning tasks evaluate a student's ability to think logically and make inferences based on verbal information. These tasks often involve identifying relationships between words, completing analogies, and deducing logical patterns.
- Pictorial Reasoning: Pictorial reasoning assesses a student's ability to analyze and draw conclusions from visual information. It involves tasks such as recognizing patterns and sequences, understanding visual analogies and identifying logical relationships within diagrams or pictures.
- Figural Reasoning: Figural reasoning measures a student's ability to manipulate and reason with visual elements, shapes, and patterns. Tasks may include identifying patterns, completing sequences, and solving visual puzzles.
- Quantitative Reasoning: This area evaluates a student's ability to understand and reason with numerical information. It includes tasks such as solving mathematical problems, recognizing number patterns and applying quantitative concepts.
- Abstract Reasoning: Abstract reasoning tasks assess a student's ability to think conceptually and solve problems using abstract symbols or ideas. These tasks often involve identifying patterns, completing sequences and making logical deductions.
- Cognitive Skills and Strategies: The OLSAT also includes items that assess a student's cognitive skills and strategies, such as mental flexibility, problem-solving approaches, and the ability to apply knowledge in new situations.
It's important to note that the specific subtests and content may vary across different versions and levels of the OLSAT.
The test is designed to provide a comprehensive assessment of a student's cognitive abilities, helping educators and administrators make informed decisions regarding educational placement and programming.
Why the OLSAT?
The OLSAT (Otis-Lennon School Ability Test) is used for several reasons in the field of education.
Here are some key reasons why the OLSAT is utilized:
-
Identification of Gifted and Talented Students: One of the primary purposes of the OLSAT is to identify students who demonstrate high intellectual abilities and are suitable candidates for gifted and talented programs.
-
Admissions to Private Schools: Many private schools use the OLSAT as part of their admissions process to assess applicants' cognitive abilities and academic potential.
-
Assessment of Cognitive Abilities: The OLSAT assesses a wide range of cognitive abilities, including verbal and non-verbal reasoning, critical thinking, abstract reasoning and problem-solving skills.
-
Educational Planning and Intervention: Schools and educators can use the test scores to identify students who may benefit from additional educational support, specialized instruction or targeted interventions to help them reach their academic potential.
-
Research and Data Analysis: The test results can be analyzed to understand trends, patterns and disparities in student performance, informing educational policies and practices.
OlSAT Test Format
The test consists of 21 different types of questions and has seven levels:
- Level A – Pre-Kindergarten and Kindergarten
- Level B – 1st Grade
- Level C – 2nd Grade
- Level D – 3rd Grade
- Level E – 4th and 5th Grades
- Level F – 6th, 7th and 8th Grades
- Level G – 9th, 10th, 11th and 12th Grades
Not all question types apply to all levels. Pictorial, verbal reasoning and following directions are for levels A to C. Levels D to G focus more on analogies, quantitative reasoning, patterns and logical selection.
Depending on the level, your child will have between 60 and 77 minutes to answer 40 to 72 questions.
For levels A, B and C, your child will be read the questions in a one-on-one setting. Older children will take the test in groups, under exam conditions.
The format of the test means that the difficult questions are mixed in with easier ones. This has been proven to keep your child's confidence up while they are taking the test.

OLSAT Test Examples
Practice OLSAT Level A with Test Prep Online
Level B & C
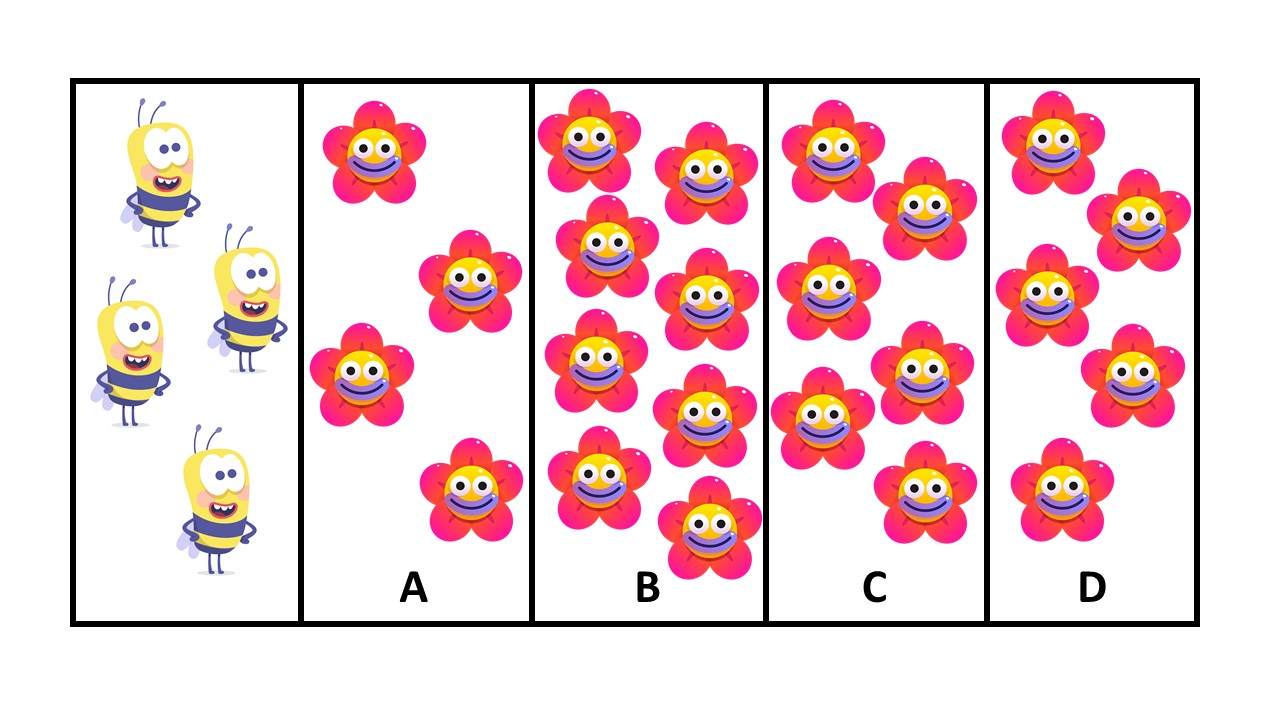
2. Can you see all the bees in the box? They each need 2 flowers each to make honey. Select the box that has all the flowers the bees need.
Practice OLSAT level B & C Test Prep Online
Level D & E
3. Which item does not belong in the list?
A) ring
B) earing
C) sock
D) bracelet
4. The opposite of ‘sad’ is:
A) upset
B) happy
C) moody
D) angry
Prepare for OLSAT Level D & E Test Prep Online
Level F & G
5. are badgers for ruthlessness their renowned Honey
Look at the sentence above. If you were to rearrange it so that it made as much sense as possible, what would the first letter be?
A) B
B) A
C) R
D) H
The correct answers are:
1. C – These letters do not match
2. B – If four bees need two flowers each, 2 x 4 = 8
3. C – All the others are items of jewellery
4. B – All the other words are synonyms and not opposites
5. D – The sentence would be ‘Honey badgers are renowned for their ruthlessness’
Practice OLSAT Level F & G Test Prep Online
If you want 12-month access to all the practice resources for this test, our partner TestPrep-Online.com offers a Family Membership.
Family Membership gives you access to all the TestPrep-Online resources for the next 12 months. You will also get two separate accounts, which can be very helpful if you have two children preparing for their tests.
Get a Family Membership with 12-month access
OLSAT Scoring
Your child's raw score will be issued first. This is simply the number of questions your child answered correctly; for example, 46 or 64.
The following result is the School Ability Index (SAI) score. This is calculated by turning the raw scores into a normalized score and using that mean number to position your child.
The SAI average mean is 100, with deviations of 16. The maximum score is 150.
Any child with a score of 132 or over is in the top 2% of the population. 116 – 132 is 14% of the population, and 84 – 116 covers 64% of the population.
OLSAT Test Preparation (2025)
As the OLSAT covers such a broad age range, different advice is recommended for each level.
It is also a complicated test. The first and most important thing you can do to prepare is to speak to other parents whose children have already experienced the test.
This is going to help a lot with your own process and will answer a lot of your questions – especially if their children sat the same level test.
Try to ask three or more parents so that you can gather a broader range of information.
Speak to your child's teacher to better understand their leaning habits, strengths and areas to develop. No one knows how your child learns better than their teachers.
Having regular conversations with teachers also keeps them updated as to what areas they should push in class.
OLSAT Levels A, B and C
-
This test measures intelligence. Therefore, the teacher will not repeat a question, regardless of the child's age. Teaching your young child to sit still and focus for longer periods will help them keep interested during their test. The younger groups have 77 minutes to answer their questions, so they need to be able to concentrate for at least an hour.
-
Children learn through play. Make the test practices part of playtime so that your child thinks it is a game and wants to take part. On test day, your child will consider the assessment as a game rather than something different and unusual.
-
Practise listening skills and try to get your child to understand that there is only one answer for each question.
OLSAT Levels D – G
-
Teaching your child discipline by creating a study schedule will help your child maintain focus and determination. It is essential to stick to the plan so your child knows what is expected of them and when.
-
Explaining the importance of the test and the impact it may have on their future will help your child to understand why they are doing all the extra work and taking tests that their friends may not be. Helping them see the bigger picture will make the test preparation less daunting if they know it leads to something.
-
Complete as many practice papers as possible. When it comes to the real test, you want your child to be 100% comfortable with the test format and the question styles. You also want your child to be aware of time, how long it takes them to process a question and roughly how long they have to spend on each question.
-
Another advantage of taking practice papers is that you can see your child's weak areas. Discussing why that answer was incorrect and spending more time studying that topic will help with the overall result of the test.
-
Teach your child to quickly identify options that can be eliminated to help with their thinking and timekeeping.
Practice OLSAT Test Test Prep Online
Tips for Solving OLSAT Classification Questions
Here are some tips to help you solve OLSAT classification questions effectively:
Identify the Rule
Carefully analyze the given set of objects and try to identify the underlying rule or pattern.
Look for similarities or differences in shape, size, color, position or other characteristics that might be relevant to the classification.
Compare and Contrast
Pay attention to the relationships between the objects in the set.
Compare each object with the others and look for commonalities or distinct features. Note any recurring patterns or groupings that emerge.
Create Mental Categories
Group the objects mentally based on shared attributes or characteristics.
Create categories or subsets that include objects with similar properties.
This will help you organize your thinking and make it easier to classify the objects.
Test Each Option
Evaluate each answer option against the established rule or pattern.
Determine whether the given objects fit into the categories you created or if they violate the observed relationships.
Eliminate answer options that do not conform to the established pattern.
Use Process of Elimination
If you're unsure about the correct classification, use the process of elimination to narrow down your options.
Eliminate choices that clearly do not fit the established pattern or violate the observed relationships.
This increases your chances of selecting the correct answer.
Check for Exceptions
Be aware of any exceptions or irregularities in the pattern.
Sometimes, there may be one or more objects that deviate from the established rule.
Take note of these exceptions and consider them when classifying the objects.
Practice Visualizing Patterns
Developing your visual pattern recognition skills can be beneficial for solving classification questions.
Practice identifying patterns and relationships in visual stimuli, such as shapes, figures or sequences.
This can help improve your ability to quickly recognize patterns in OLSAT classification questions.
Time Management
OLSAT tests are typically timed, so it's important to manage your time effectively.
Don't spend too much time on a single question.
If you're unsure about the classification, make an educated guess and move on to the next question. You can always come back to it later if time allows.
General Tips for OLSAT Test
Studying and completing practice papers is a great way to prepare, but your child needs to be fit and healthy to perform at their best.
Regular exercise and a well-balanced diet will help with concentration and energy levels. Frequent breaks from studying and good sleeping patterns also help with energy, motivation and memory.
But most importantly, your child should never be stressed out by this test to the point where it is affecting their sleep patterns and appetite.
Should My Child Take the OLSAT Test?
This test is very trying and designed to identify those students with highly developed reasoning skills and intelligence.
This means that your child needs to be excelling across all subject areas and in everyday life.
Just because your child is particularly good at maths or was quick to learn the alphabet, doesn't mean they are an ideal OLSAT candidate.
Speaking to your child's teacher is a great place to start as they see the behaviours of those exceptional students. If you have a young child, the teacher may suggest waiting a year or two to see how they develop. For older students, the teacher should have an idea of their intelligence.
Allowing your child to try a practice test will also give you a good indication.
Start a level down to build your child's confidence before letting them try the paper for their age group. If they seem ok with the questions, then start the process.
Final Thoughts
Remember, this test can be taken at every age group, so there is no rush to have your child sit it. If taking the OLSAT a year later will yield a better result, then choose that option.
Getting children into programs that suit their level and style of learning is so important.
These and other tests help to identify those that could benefit from accelerated learning.
But this is a test for exceptional students, and should only be considered if you and your child's teacher think it is the best option for your child.








